Sciatica is a common problem that affects half of all people at least once in their lives. It is a pain in the lower back that results from compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve – the largest nerve in our body. This pain can spread from the lower back, through the buttocks, all the way to the toes. Although sciatica often begins as a mild discomfort, it can quickly develop into severe and limiting chronic pain that makes even simple activities impossible.
What exactly is sciatica?
The sciatic nerve (nervus ischiadicus) is the longest and thickest nerve in our body, its nerve roots originate in the lumbar spine, running through the pelvis to the feet on both sides of the body.
The sciatic nerve is a sensory and motor nerve, which means that it transmits messages about sensation on the skin (the entire back of the leg, the outside of the foot, the sole of the foot) and about movement of the muscles of the lower body (hip, knee, ankle, foot). The location of the nerve compression causes sensory and motor function loss of various parts of the lower body.
Sciatica is a term for a group of symptoms caused by compression of the sciatic nerve (nervus ischiadicus).
The typical symptoms of sciatica are acute and stabbing pain that radiates from the lumbar spine through the buttocks down the back of one or both legs. Isolated pain exclusively in the leg or legs is also present. Sciatica usually affects only one side of the body.
Symptoms of sciatica and how to recognise it?
Sciatica symptoms vary in intensity depending on the location and the degree of the sciatic nerve compression. The most common sensations are:
- Sharp and burning pain that spreads through the buttocks all the way to the toes.
- The pain is occasionally present only or in isolation in a lower extremity.
- The pain typically worsens during sitting.
- A feeling of tingling and numbness (like being pricked by a thousand needles).
- Muscle weakness in the lower extremities (making it difficult to walk, stand for long periods of time, and lift objects).
- Reduced flexibility and mobility in the spine and lower body.
- Loss of sensory and/or motor reflexes in the lower body.
Weakness in the affected lower extremity and difficulty moving the leg and foot are typical symptoms, which, as mentioned above, can progress to major neurological pathologies in later stages.
Progressive forms of sciatica symptoms can lead to foot drop or loss of neurological function of the foot.
Severe compression of the sciatic nerve causes bladder problems, leading to urinary incontinence or difficulty urinating.
Did you know that sciatica rarely occurs before the age of 20, and most often occurs between the ages of 40 and 50?
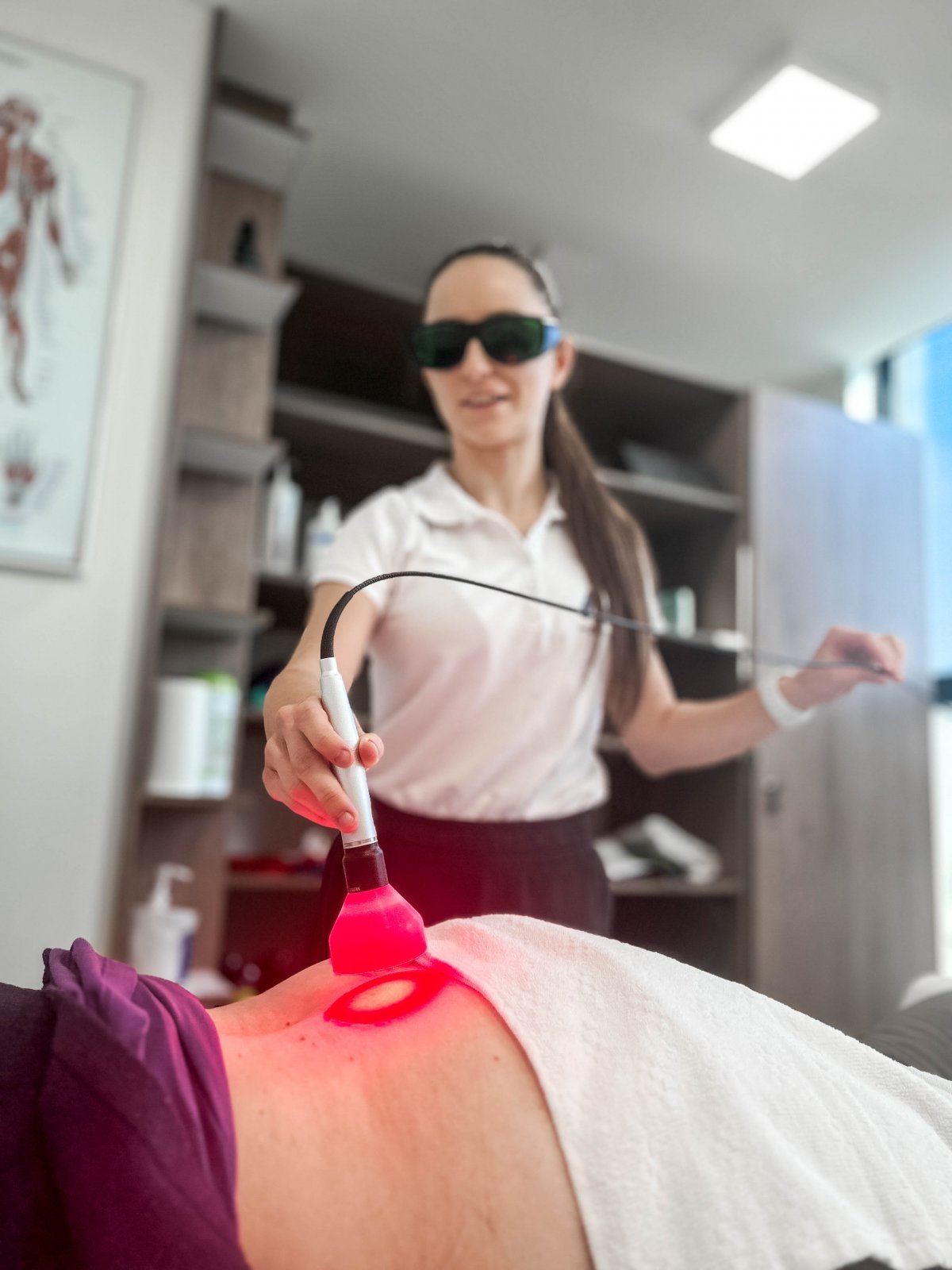
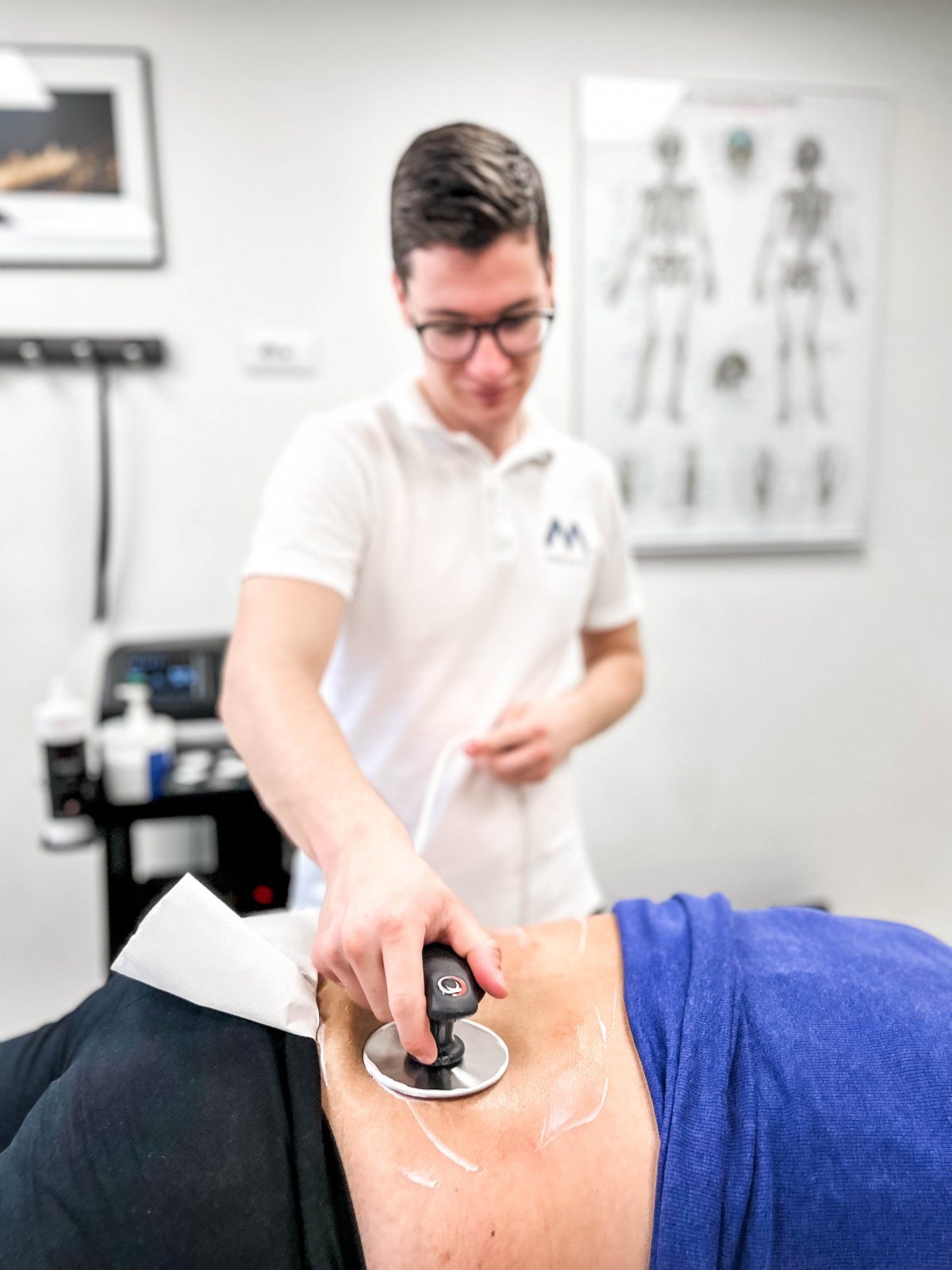
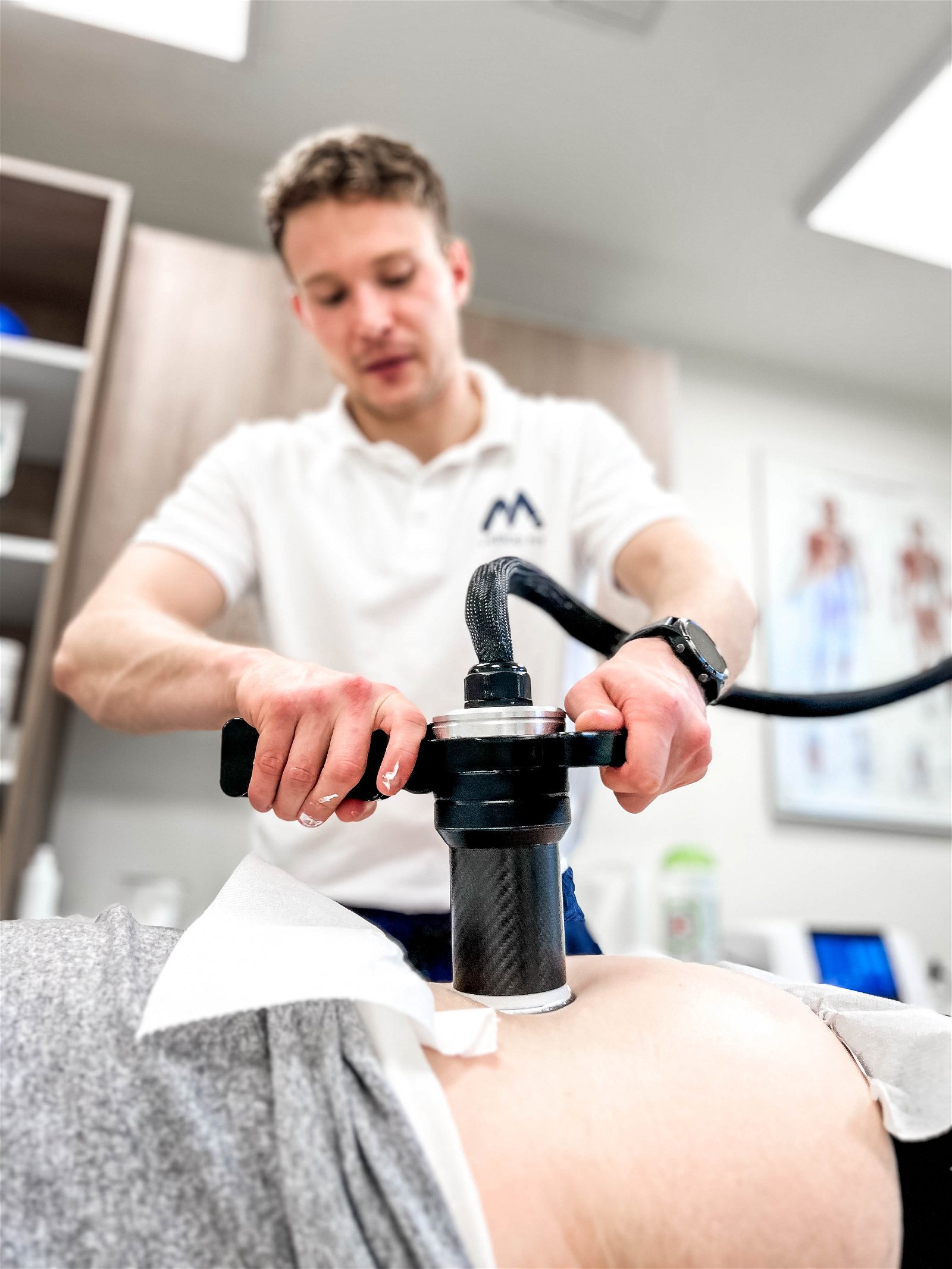
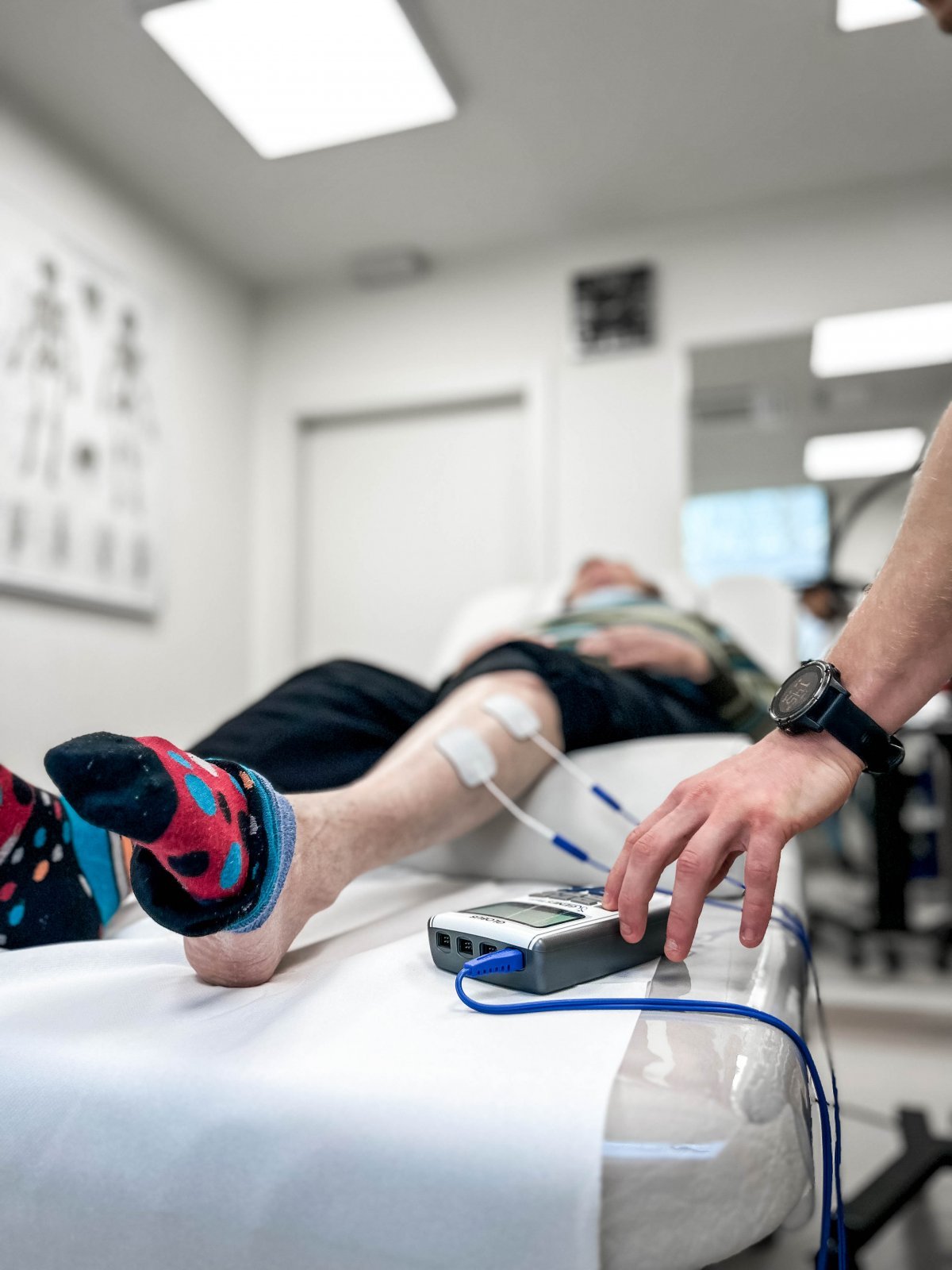
WHEN TO OPT FOR MEDICOFIT DIAGNOSTIC THERAPY?
- Persistent pain in the lower back that spreads into one or both legs.
- Presence of neurological symptoms such as weakness, numbness, or tingling in the legs.
- If you have previously had problems with low back pain and the symptoms are recurring, this means that the low back pain was not properly treated.
At MEDICOFIT clinic, we provide patients with scientifically supported specialist physiotherapy for herniated disc, which begins with booking a diagnostic therapy appointment.
Make an appointment for low back pain treatment
How does sciatica occur?
Sciatica occurs when the nerve roots of the sciatic nerve become compressed due to various factors:
- A herniated disc is a protrusion of the soft core of the intervertebral disc into the fibrous ring that surrounds it (the soft core) that then presses on the protruding nerve root.
- Spinal stenosis is a medical condition that causes the spinal canal (central nervous system) to narrow, which results in compression of the sciatic nerve.
- Degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs, which are most often a result of ageing, cause the vertebrae to collapse, which compresses the sciatic nerve and causes sciatica pain.
- Spondylolisthesis is the movement or slippage of a vertebra forward, which means that the alignment with the other vertebrae is disrupted. A slipped vertebra causes compression of the sciatic nerve and, as a result, sciatica pain.
- Piriformis syndrome describes the stiffness and inflammation of the piriformis muscle, which is located deep in the gluteal region. The sciatic nerve runs through or next to the piriformis muscle, and when the muscle tightens, the nerve becomes compressed, causing sciatica pain.
- A traumatic injury (fall, car accident, direct blow to the spine, sports injury) causes compression of the sciatic nerve.
- Sciatica during pregnancy is a common condition that affects pregnant women due to hormonal changes, spinal pathologies, being overweight, and rapid uterine enlargement.
The true cause of sciatica is determined during the initial diagnostic examination, which is the basis for determining an individualised treatment programme for sciatica pain.