Frequently asked questions about sciatica
1) What kind of pain causes sciatica ?
Symptoms of sciatica (sciatica pain) occur suddenly, with a jolt on movement, with an aggressive pain response in the back, buttocks and legs, or gradually due to the progression of degenerative changes in the spine. Sciatica can also occur without pathology, in which case the pain diminishes rapidly
2) How does sciatica feel ?
Sciatica is caused by a strong acute irritated condition. The pain is intense and may be accompanied by neurological symptoms in the lower limbs, e.g. tingling in the legs and feet, as well as sensations of hot or cold feet. In advanced states of sciatica, sensory and motor disturbances of the legs may also occur.
Sciatica is distinguished from normal back pain by the pain spreading to the buttocks, hips and down the legs or feet. Sciatica is characterised by occurring on only one side of the body, although in rare cases it can occur bilaterally.
3) Can sciatica occur in both legs ?
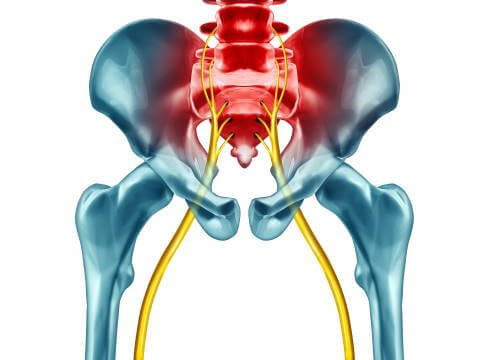
Sciatica can occur in both legs, usually as a result of a compression at the level of the lumbar spine in the form of a broad-based disc herniation, where the sciatic nerve roots are affected bilaterally. Sciatica in both legs can occur when there are multiple associated pathologies of the lumbar spine, e.g. disc herniation at two levels of the spine on different sides, or disc herniation with arthritic changes on different sides. It is also common for sciatica to be felt bilaterally in an extremely acute condition.
4) Does sciatica occur immediately or gradually ?
Sciatica can occur when a movement is ”incorrectly” performed, although in reality it is not an incorrect movement. It is the poor activity of the muscle groups at the moment of the movement, with the probable presence of degenerative changes in the form of disc herniation or other pathologies. Often, the ”incorrect movement” is only the trigger of the sciatica symptoms, but the problem is broader than that.
5) How quickly does sciatica resolve ?
Sciatica can resolve quickly, within 1 week , in some cases, although in most cases the symptoms persist for several weeks. Sciatica can persist for months or years, depending on the approach of the individual. With proper physiotherapy and kinesiology, which is recommended for all sciatica patients, the pain usually resolves completely within a window of 6 – 12 weeks.