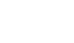Everyone has woken up and felt stiffness in the neck that has limited normal movement or daily functioning or developed during the day after a physically strenuous activity such as moving a heavy wardrobe or playing sport.
Waking up with a stiff neck (german: hexenschuss) is annoying but not necessarily dangerous. A stiff neck is usually caused by muscles in the neck or by a medical condition such as osteoarthritis, which affects the spinal facet joints. Find out below when the symptoms of stiff neck are dangerous to your health.
Anatomy of the cervical spine
The spine is crucial for our basic movement and walking, giving us structure and support. At the same time, it provides protection for the spinal cord, which is part of the central nervous system that allows functional movement and normal functioning of the internal organs.
The cervical spine is the most mobile part of the entire spine. The cervical spine begins just below the skull and contains 7 cervical vertebrae that occupy the lordotic curve. The special feature of the cervical vertebrae is their anatomical structure, which, in addition to the main opening for the spinal cord, contain the openings for the arteries that carry blood from the heart to the brain.
An additional feature of the cervical spine is the first and second cervical vertebrae, called the atlas (first vertebra) and the axis (second vertebra). Their anatomical structure allows for a greater range of movement of the neck, especially rotational movement.
The mobility of the cervical spine poses a greater risk of musculoskeletal injuries due to the physical shape of the vertebrae, which are smaller and subjected to the additional weight of the head, and the reduced muscular support (1).
What are the symptoms of a stiff neck?
Severe neck pain is manifested as restricted movement (turning the head one way or the other is a particularly restricted movement), stiffness and pain. Restricted movement in the neck makes it necessary to turn the whole body, which affects the performance of everyday activities such as driving.
The degree of pain experienced by an individual is subjective and therefore varies in its intensity. Individuals describe the pain of a stiff neck as sharp or blunt.
Muscle contraction puts pressure on a nerve originating from the spinal cord in the cervical spine, causing tingling, a numb sensation and a burning pain radiating into the arm.
Associated symptoms of stiff neck are headache and shoulder pain (2).
How long does a stiff neck last?
Stiff neck’s symptoms disappear over a period of time ranging from one day to one week. The treatment time depends primarily on your treatment approach. The correct treatment approach for stiff neck’s symptoms affects the level of pain and reduces the chance of the condition recurring.
What does it mean if the symptoms of stiff neck last longer than one week? A visit to the doctor is recommended.
What are the causes of stiff neck?
The development of neck pain is caused by one or a combination of different factors that influence the development of symptoms, which we present to you in more detail.
- SLEEP is the most common cause of a stiff neck. Improper sleeping position, mattress and inadequate pillow are the main reasons why a person wakes up with a stiff neck.
- ACCIDENTAL INJURY that occurs during sport or everyday tasks, such as falling and side impact to the neck.
- LONG-TERM REPEATED POSITIONS during various activities that put strain on the neck muscles, such as working on a computer or swimming.
- POOR POSTURE has a negative effect on the entire spine. During prolonged use of the phone, the cervical spine is in a position where you are looking towards the floor. This position causes stresses on the anatomical structures in the cervical spine, which over time develop various pathologies

- STRESS (physical, mental, financial, etc.) you experience in your daily life has an impact on the stiffness of your neck. You have probably heard the metaphor “you carry the whole world on your shoulders”, this represents the stress-related stiffness that is physically reflected in your body.
- EVERYDAY POSITIONS that you perform automatically are the most damaging to you, because you are not even aware of them (e.g. talking on the phone – holding the phone between your ear and shoulder).
- JOINT DISORDERS such as osteoarthritis are the cause of stiffness in the neck.
- CENTRAL VASCULAR SYSTEM INJURY is a serious pathological condition that results in neck stiffness. If inflammation of the spinal cord or brain is suspected, a visit to a doctor is urgently needed (3)(4)(5).
Stiff neck symptoms are most often treated in home care and below we present effective ways to relieve neck pain and improve range of motion.
The primary recommendation is to rest for a day or two. During the rest period, we allow the tissue the ability to heal properly. Rest reduces pain, muscle shrinkage in the neck and stiffness. Prolonged rest and consequent muscle inactivity leads to loss of muscle mass and muscle weakness, which worsens the symptoms of stiff neck and creates additional problems.
Until further notice, avoid ACTIVITIES THAT WORSEN YOUR PAIN, such as excessive use of the computer, telephone, swimming, etc.
For the first two to three days, the use of COLD (cryotherapy) is recommended in order to reduce inflammation and muscle pain. Later, the use of HEAT (thermotherapy) is recommended as it increases blood flow and reduces muscle stiffness in the neck.
It is recommended to stretch the neck muscles in a NON-INTENSIVE way, for which we suggest that you learn how to stretch correctly with the help of a physiotherapist.
You can watch the basic examples of exercises TO INCREASE MOBILITY IN THE NECK and start doing them right away.
EXERCISE 1 – FLEX YOUR HEAD FORWARD (FLECTION): Slowly bring your jaw to your chest and look towards the ground.
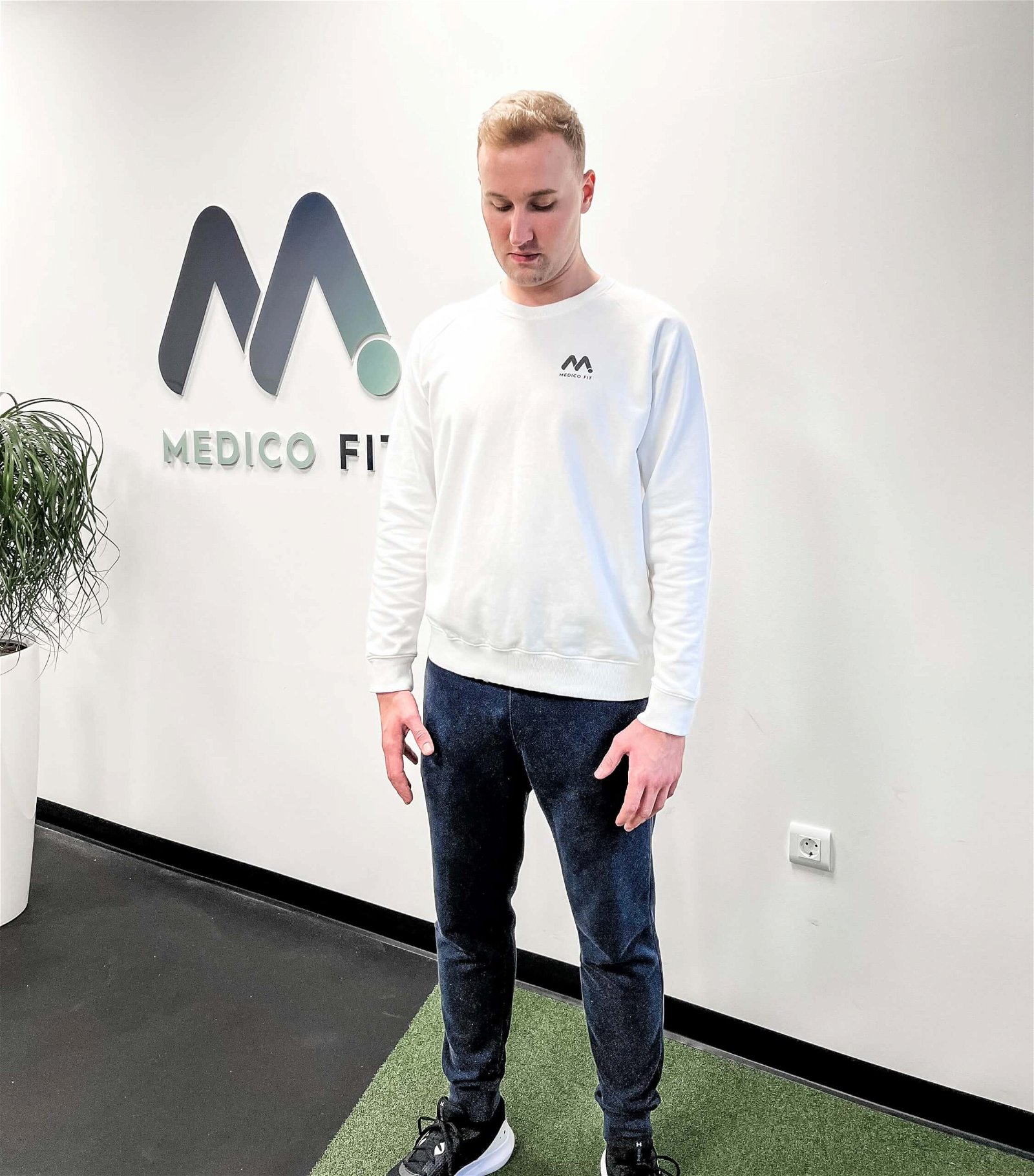

EXERCISE 2 – EXTENDING THE HEAD BACK (EXTENSION): Slowly bring the back of your head to the back of your chest and look up towards the ceiling.
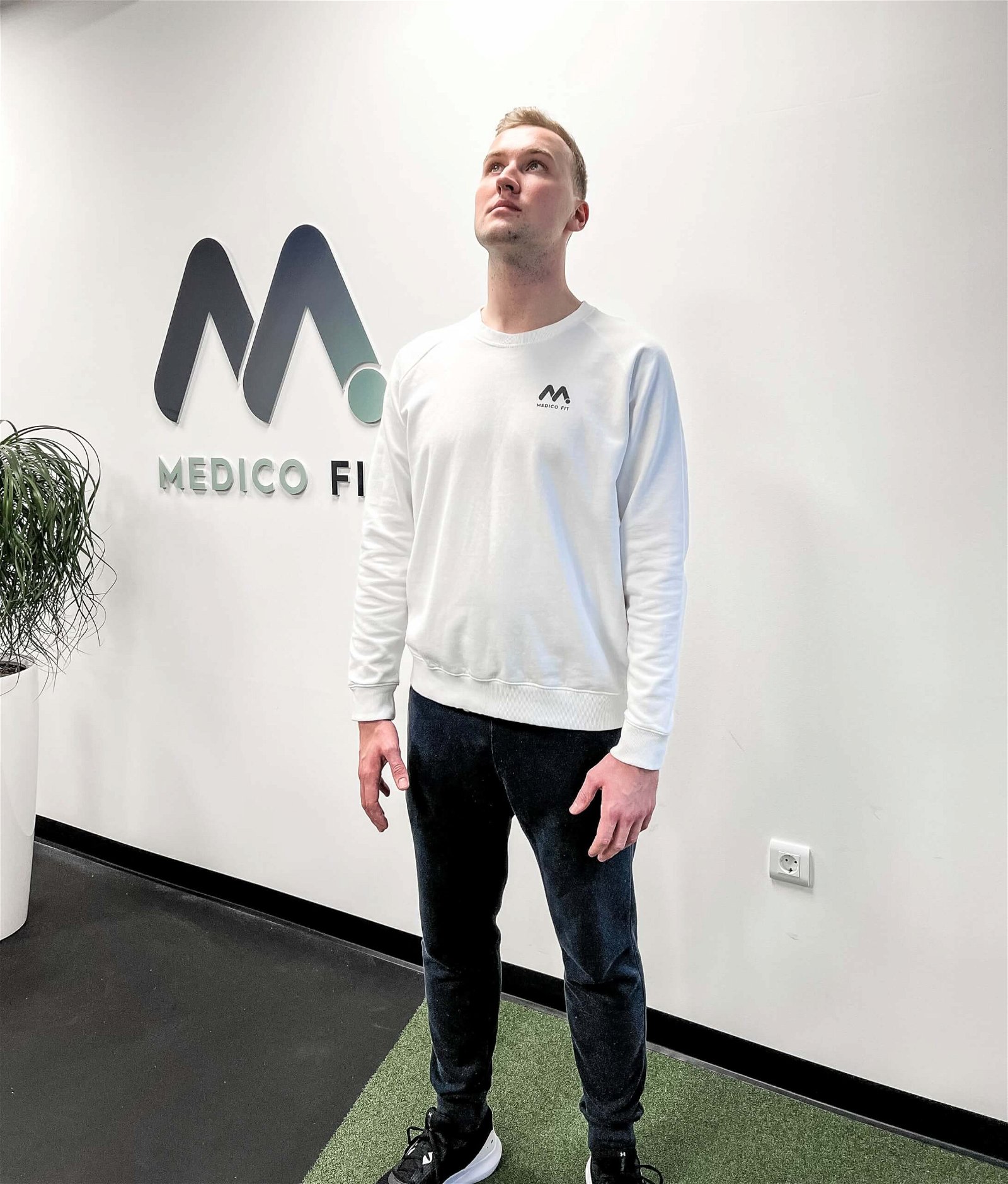

EXERCISE 3 – LATERAL FLEXION: Slowly bring the left ear to the left shoulder (repeat on the other side).
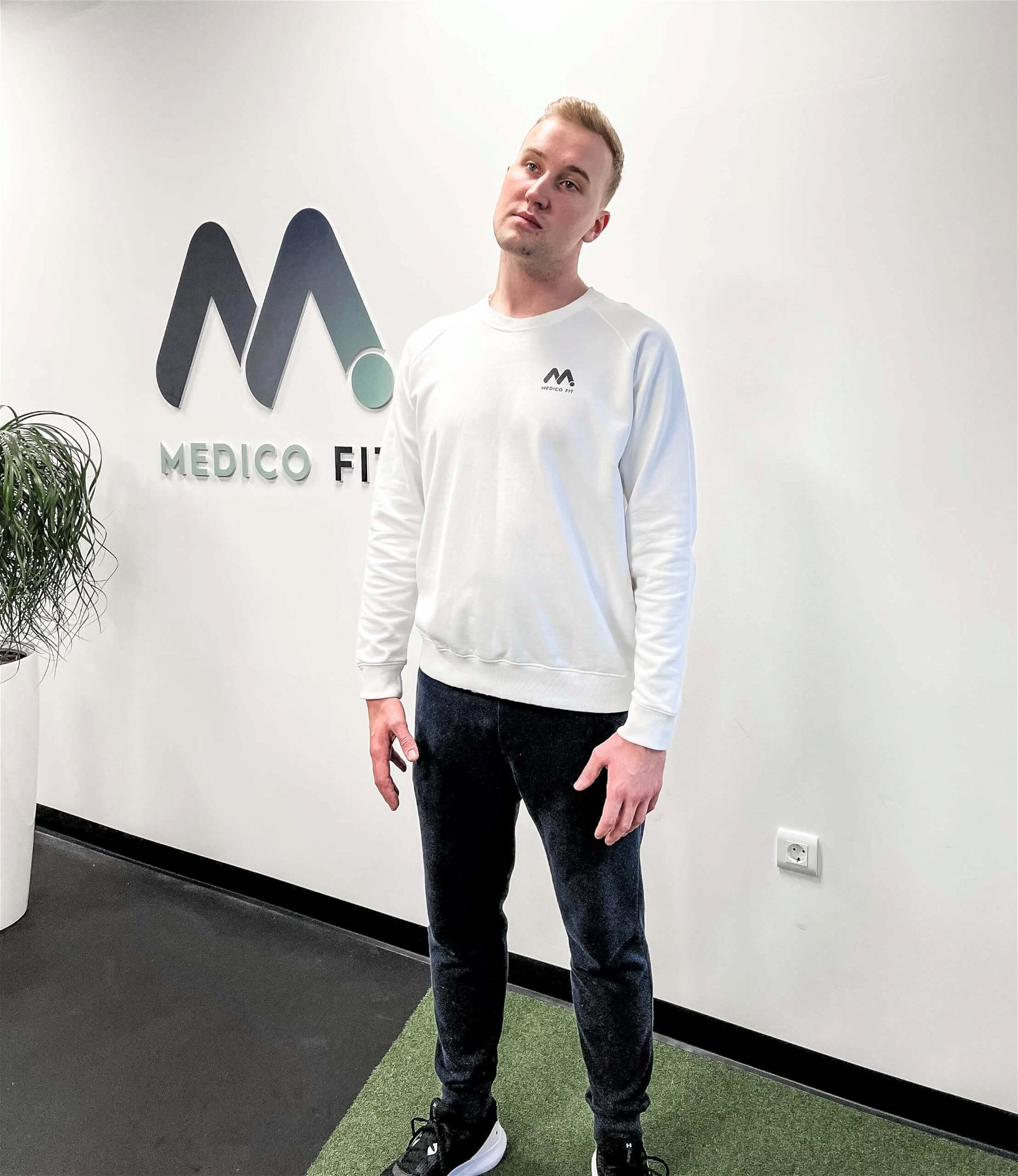

EXERCISE 4 – ROTATE IN ONE DIRECTION: Slowly bring your chin towards your shoulder and look in one direction over your shoulder (repeat in the other direction).

How MedicoFit experts successfully reduce the chances of developing a stiff neck
Anyone who has ever experienced a stiff neck would like to know the secrets of how to reduce the chances of getting one.
At MedicoFit private clinic, we understand the importance of quality prevention to prevent potential injuries and we are revealing our secrets to reduce the chances of a stiff neck.
Our work focuses on establishing the appropriate loading capacity of the cervical spine and the biomechanics of posture.
What this actually means, what modern concepts of treatment and prevention look like, and what impact this has on the body, we want to bring you up to speed below
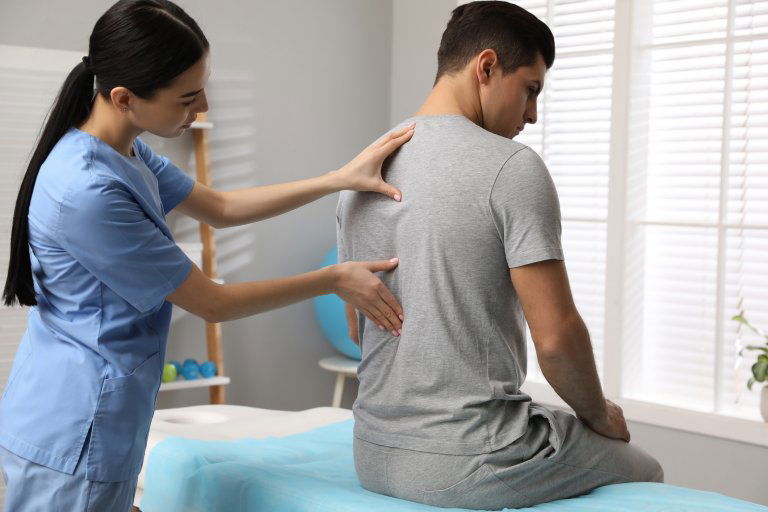
Physiotherapy treatment for stiff neck
The initial phase of physiotherapy treatment involves a diagnostic examination to gain insight into the physical condition of your body, the cause of the problem, the consequences of the disease and the limitations it brings.
The diagnostic physiotherapist sets an individual physiotherapy programme which focuses on correcting or controlling the symptoms and maintaining general physical function. We focus on reducing pain, stiffness in the neck, improving range of motion, strengthening the musculature and developing dynamic stability in the neck.
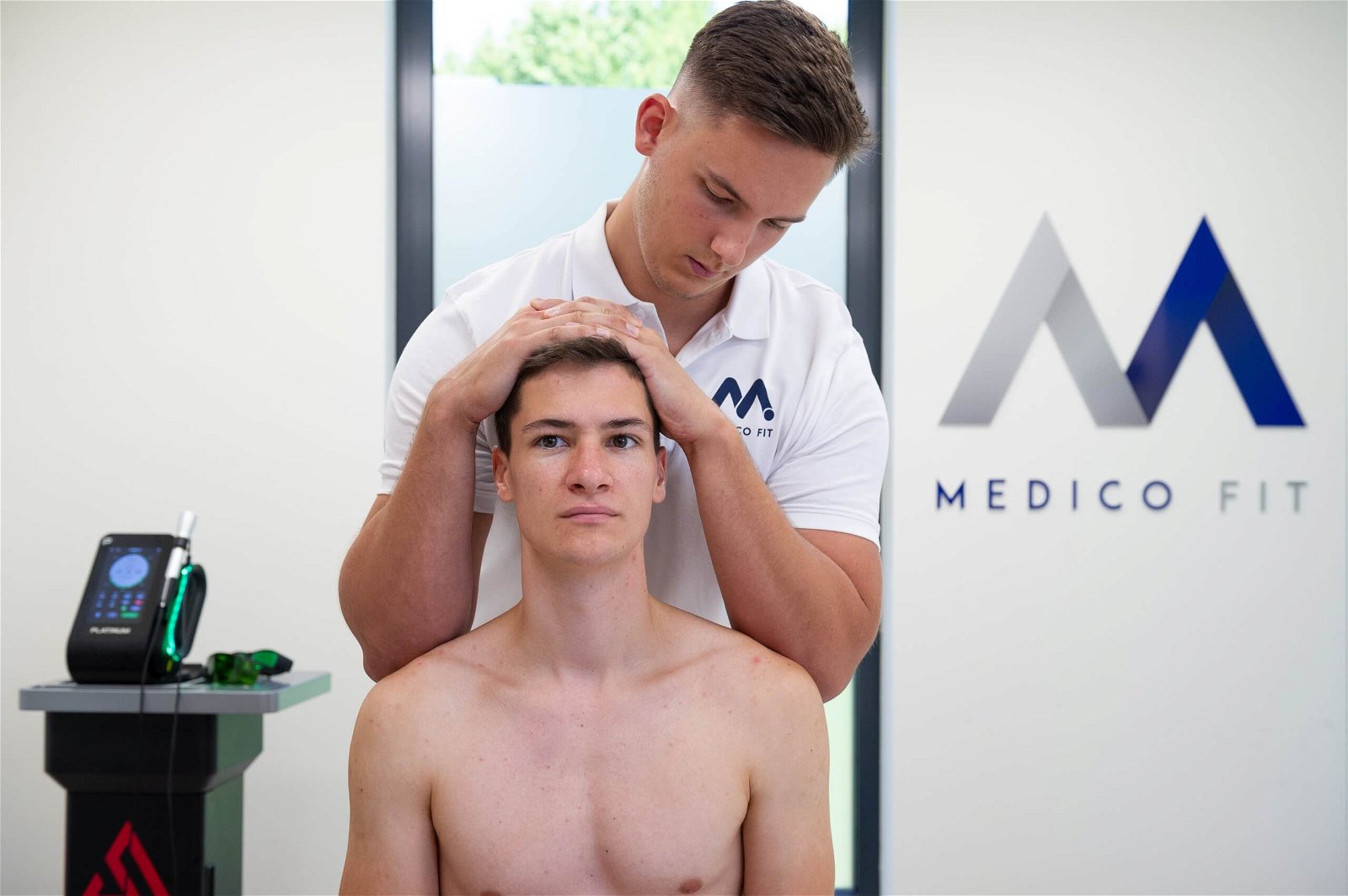
Kinesiology training is a key part of physiotherapy treatment, as we achieve strengthening and flexibility of the neck muscles through stretching and active exercises. Strengthened muscles in the neck are able to withstand the daily stresses of tension more efficiently.
Modern physiotherapy treatment contains a key element to which special attention is paid – the restoration of the correct load capacity of the spine. It is important that your cervical spine is able to perform appropriate movements within its full range of motion.
We first perform isometric exercises and later active exercises for the cervical and spinal musculature, which are crucial for the correct biomechanics of posture.
Physiotherapy treatment includes the use of kinesiotaping and massage, in addition to state-of-the-art assistive technology such as ultrasound therapy, laser therapy and TECAR therapy.
The physiotherapist will advise you on the correct layout of your working environment, the correct ergonomic position, the correct way to get out of bed, the correct way to pick up heavy items, etc.
His/her task is to raise your awareness and promote your own awareness of how to carry out your daily activities in proportion to the correct spinal positions and posture.
When to see a doctor?
As mentioned above, a visit to the doctor is necessary when symptoms last longer than a week. A visit to the doctor for stiff neck is necessary when there is associated fever, severe headache, vomiting, dizziness, loss of coordination and balance (2).
- Kelc R., 2012. Funkcionalna anatomija hrbtenice. VIII. Mariborsko ortopedsko srečanje. Interdisciplinarno strokovno srečanje. Hrbtenica v ortopediji. Zbornik predavanj. Maribor, pp. 13-23
- Cohen S. P. (2015). Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of neck pain. Mayo Clinic proceedings, 90(2), 284–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.09.008
- David D, Giannini C, Chiarelli F, Mohn A. Text Neck Syndrome in Children and Adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(4):1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041565
- Perolat, R., Kastler, A., Nicot, B. et al. Facet joint syndrome: from diagnosis to interventional management. Insights Imaging 9, 773–789 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-018-0638-x
- Kazeminasab S, Nejadghaderi SA, Amiri P, Pourfathi H, Araj-Khodaei M, Sullman MJM, Kolahi AA, Safiri S. Neck pain: global epidemiology, trends and risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Jan 3;23(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04957-4. PMID: 34980079; PMCID: PMC8725362.