-
Bouchard’s nodes
-
Dupuytren’s contracture
-
Heberden’s nodes
Bouchard’s nodes are bony enlargements of the middle joints of the fingers, also known as the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints. These are the finger joints located in the middle of the knuckles. Bouchard’s nodes are not painful by nature, but they are likely to increase pain that occurs with movement.
Bouchard’s nodes are a classic sign of osteoarthritis or degeneration of the hand joints, but they are seen much less frequently in practice than Heberden’s nodes.
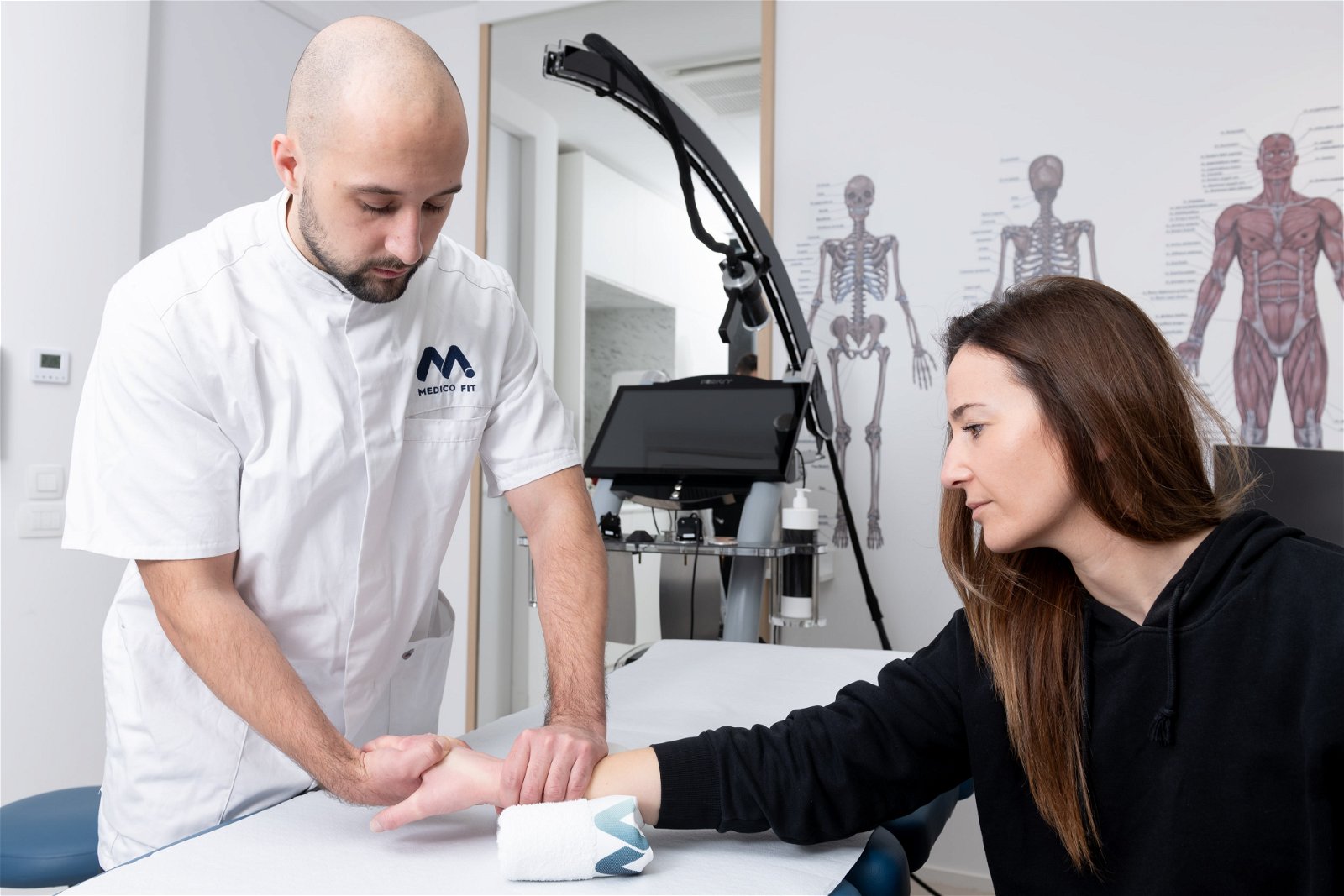
We successfully treat Bouchard’s nodes as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for palms and fingers.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for palm/fingers >>
Dupuytren’s contracture is a connective tissue disease that affects the palms – especially the fingers. It is a gradual narrowing and shortening of the fascia under the skin of the palm and fingers, which causes the fingers to curve towards the palm.
The thumb, index finger, and middle finger are most frequently affected. In the initial stages, only a small lump or nodule may appear on the palm, which over time can enlarge and cause shortening of the tendons, leading to limited finger mobility.
We successfully treat Dupuytren’s contracture as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for palms.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for palm/fingers >>
Heberden’s nodes are small, pea-sized bony growths that appear on the joint closest to the tip of the finger, also called the distal interphalangeal (DIF) joint. Heberden’s nodes are a typical symptom of hand osteoarthritis.
When osteoarthritis affects your hands, the joints in your fingers can become stiff and painful – the rough bone no longer slides as smoothly as cartilage.
We successfully treat Heberden’s nodes as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for palms and fingers.