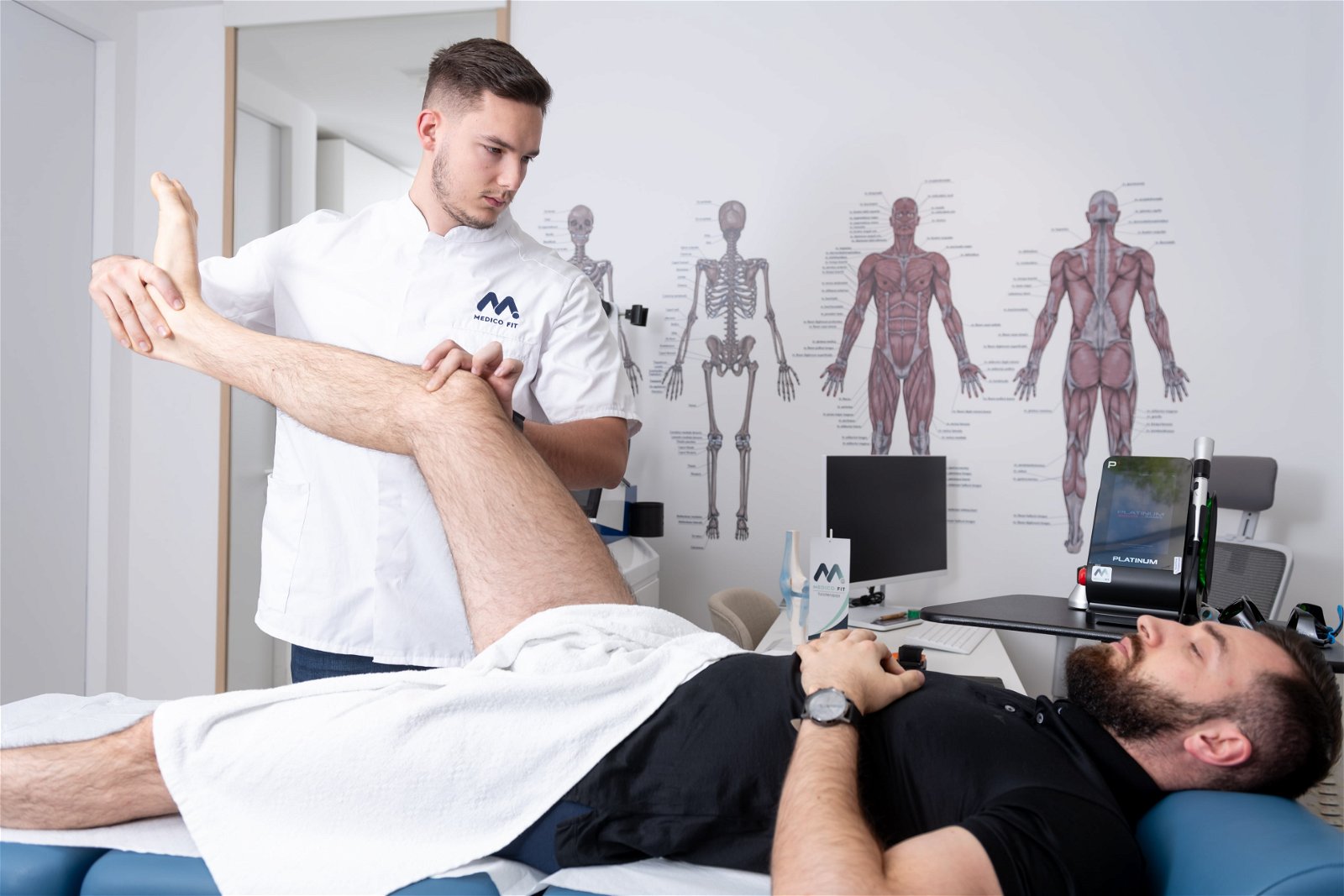
-
Denuded cartilage with subchondral oedema
-
Discoid meniscus
-
Gonarthrosis (arthrosis of the knee)
-
Chondromalacia patellae
-
Tibial plateau chondropathy
-
Articular cartilage chondropathy
-
Incarceration of the meniscus
-
Lateroposition of the patella
-
Cyclops lesion
-
Kissing lesions
-
Lateral subluxation of the patella
-
Medial tibial stress syndrome (MTSS)
-
Meniscocapsular separation
-
Meniscopathy with a fissure
-
Mucoid degeneration of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
-
Parameniscal cyst
-
Patella alta
-
Patellofemoral arthrosis
-
Pellegrini-Stieda lesion
-
Perimeniscal cyst
-
Pes anserinus bursitis
-
Pivot shift injury
-
Post-contusion lateral condyle oedema
-
Proliferative patellar ligament enthesopathy
-
Ramp lesion
-
Resection of parapatellar/infrapatellar plica
-
Lateral collateral ligament rupture
-
Medial collateral ligament rupture
-
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease
-
Segond fracture
-
Synovial infrapatellar plica
-
Stieda fracture
-
Patella fracture
Denuded cartilage refers to a condition in which the articular cartilage is completely worn down or removed, exposing the underlying subchondral bone. Subchondral oedema, which refers to swelling and increased fluid in the bone tissue just below the articular cartilage, is also usually present. Both conditions are usually the result of degenerative processes or acute injuries to the joint.
Denuded cartilage is successfully rehabilitated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
This is a developmental abnormality of the meniscus, where the meniscus is unusually disc-shaped instead of the normal crescent shape. This anatomical variation is most often present in the lateral meniscus and can cause pain, swelling, and “snapping” in the knee. The condition can become symptomatic, especially with injuries.
Discoid meniscus is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Gonarthrosis – wear of the knee joint due to gradual degeneration of cartilage – is the technical term for osteoarthritis of the knee, where the knee wears out. Knee bones are covered with a thin layer of cartilage, which acts as a cushion where the parts of the joint come into contact. When it wears down, the bones rub against each other, causing pain and reducing mobility.
Gonarthrosis develops either in the joint between the femur and the patella (35% of cases) or in the joint between the femur and the tibia (65% of cases). If the entire joint is affected, we call it tricompartmental gonarthrosis. Osteoarthritis of the knee is a chronic progressive disease that often affects both knees at the same time.
Gonarthrosis is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee>>
Chondromalacia patellae is a common disease that causes softening of the cartilage in the patellofemoral joint. The patella is covered with a layer of smooth cartilage that normally glides gently over the knee when the joint bends. The pain is caused by irritation of the underlying surface or patella of the knee, as it rubs against the knee joint, irritating the cartilage surface.
Symptoms of chondromalacia include knee tenderness and pain that increases after prolonged sitting, using stairs, or after intense activities. When the knee is straightened, a grating sensation or crepitus may also occur.
Chondromalacia usually affects young, athletically active, otherwise healthy individuals due to overuse, injury, or excessive load on the knee. People who have suffered a sprain, fracture, or other knee injury are more prone to chondromalacia than other individuals.
Chondromalacia is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Tibial plateau chondropathy is a degenerative condition of the articular cartilage that covers the upper surface of the shinbone (tibia) where it meets the thighbone (femur) in the knee joint. This condition refers to injuries, softening, or degeneration of the cartilage of the tibial plateau, which can lead to pain, swelling, and limited mobility of the knee joint.
Tibial plateau chondropathy is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Articular cartilage chondropathy is a condition involving damage, wear, or degeneration of the cartilage in the joint. Cartilage acts as a smooth coating on the ends of bones, allowing smooth and painless movement of the joint.
In chondropathy, cartilage can become thin, crack, or even completely destroyed, which can lead to pain, stiffness, swelling, and limited joint mobility. It most commonly affects the knee.
Chondropathy of the knee joint is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >> >>
Incarceration of the meniscus is a serious injury where the meniscus tears and becomes stuck or pinched in the joint – often resulting in a condition called “locked knee”. Incarceration of the meniscus can cause severe pain and limited mobility of the knee joint.
It most often occurs in more severe meniscus injuries, where there are larger tears that can become folded or trapped within the joint. For more severe tears, arthroscopic knee surgery is often necessary.
Meniscus injuries are successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Lateroposition of the patella is a condition in which the kneecap (patella) is displaced outward (laterally) from its normal anatomical position in the knee joint. This shift can lead to improper function of the knee joint and cause pain and other mobility problems.
It is necessary to perform exercises to strengthen the quadriceps and other muscles around the knee, especially vastus medialis obliquus, and to improve the biomechanics of the lower extremity.
Lateroposition of the patella is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment >>
This term is used to describe the presence of opposing osteochondral lesions (cartilage and bone lesions) on the articular surfaces of the knee that “kiss” each other, usually due to forceful impacts or dislocations.
This condition is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
This term is used to describe the presence of opposing osteochondral lesions (cartilage and bone lesions) on the articular surfaces of the knee that “kiss” each other, usually due to forceful impacts or dislocations.
This condition is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
This is a partial dislocation of the patella towards the outside of the knee. This subluxation can occur due to weakness of the medial structures (medial patellofemoral ligament) or due to increased lateral force. It causes pain in the front of the knee and a feeling of instability, especially when bending or extending the knee.
This condition is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Also known as “shin splints”, this condition involves pain along the medial edge of the shinbone and is the result of overuse of lower extremities, often occurring in runners or jumpers. Although MTSS usually occurs in the lower shinbone, it is important to know that it can also cause pain and discomfort around the knee.
This condition is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
This is a separation of the meniscus from its attachment site on the joint capsule. It most commonly occurs in the medial meniscus and is often associated with anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries. This condition can cause pain and instability in the knee and often requires arthroscopic surgery for reattachment.
This condition is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Meniscopathy with a fissure is a condition that involves damage to the meniscus in the knee joint, resulting in a crack (fissure) in the meniscus tissue. The meniscus are two fibrocartilaginous discs (medial and lateral) located between the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia), and acting as shock absorbers and stabilisers of the knee joint. After an injury, rehabilitation is necessary to restore function.
Meniscopathy with a fissure is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
This is a condition where degenerative changes occur within the posterior cruciate ligament and involve the accumulation of mucoid material. This leads to thickening and reduced function of the ligament, which can cause pain and limited mobility of the knee.
This condition is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Parameniscal cysts are a very common finding on MRI scans of the knee. The word “parameniscal” means “next to the meniscus”. A cyst is a small sac filled with fluid.
Cysts near the lateral meniscus are usually smaller than those near the medial meniscus, as the very tight ITB (iliotibial band) restricts the growth of cysts on the outside of the knee.
Parameniscal cysts are successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Patella alta is a condition where a person is born with a high-riding patella, which is positioned higher than average in the front of the knee. Individuals with patella alta are often good athletes and do well in high jump or basketball. The problem with a high-riding patella is that it is consequently very mobile and prone to dislocation during sporting activities.
The condition where the patella repeatedly slips out of place is called recurrent dislocation and can be a major nuisance for an athlete, causing them to abandon all sporting activities. In some individuals, the dislocation of the patella is incomplete and is called a subluxation.
A high-riding patella is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Patellofemoral arthrosis is a form of knee arthrosis that affects the back (posterior) part of the patella and the channel-like groove in the femur that the patella rests in. It causes pain mainly in the front part of the knee and can make it difficult to kneel, squat, and climb or descend stairs.
Additionally, you may feel a grating sound, called crepitus, when you move your knee. Crepitus is sometimes painful and can be loud enough for other people to hear. As the disease progresses, the patella may catch when you straighten your knee.
Patellofemoral arthrosis is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Pellegrini-Stieda lesions refer to ossified post-traumatic lesions on (or near) the medial collateral ligament, which is located along the edge of the medial condyle of the femur. One of the suspected mechanisms of injury is a
Stieda fracture (avulsion injury to the medial collateral ligament at the medial condyle of the femur). Calcification usually begins forming a few weeks after the initial injury.
This condition is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Perimeniscal cysts are small cysts that form within the meniscus, and can be a completely incidental finding on an MRI scan. They are often associated with a meniscus tear, usually a degenerative type. A tear creates a one-way valve mechanism: synovial fluid from the knee joint passes through the meniscus tear into the cyst, but cannot return to the joint.
As many as 90% of perimeniscal cysts are located in the lateral meniscus, usually anteriorly. Perimeniscal cysts are found in approximately 5% of the general population.
Meniscal cysts are successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Pes anserinus bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa located between the shinbone (tibia) and the three tendons of the hamstring muscles, at the insertion point on the medial side of the knee. It occurs due to irritation and inflammation of the bursa, which then produces too much fluid, causing it to swell and put pressure on neighbouring parts of the knee.
It is characterised by pain and tenderness on the medial side of the knee, approximately 3–5 centimetres below the knee joint. Pes anserinus bursitis usually develops due to excessive load or constant friction (often in runners). Individuals with knee osteoarthritis are also slightly more susceptible to pes anserinus bursitis.
Pes anserinus bursitis is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
A pivot shift injury refers to a combined injury to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), and joint capsule that occurs due to rotation and translation of the knee. It is a complex injury that causes instability and often requires surgical reconstruction.
This condition is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Post-contusion lateral condyle oedema refers to swelling on the outside of the condyle, the lower end of the thighbone (femur), which forms the knee joint. This type of oedema can occur after an injury or contusion, such as a sprain or blow to the knee.
Oedema is the result of fluid accumulation in tissue in response to injury. In the case of post-contusion lateral condyle oedema, this fluid accumulates on the lateral side of the condyle, which can cause swelling, pain, limited mobility, and discomfort in the knee.
Post-contusion oedema is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Enthesopathy is a term describing problems with the attachment of tendons or ligaments. It is a disorder of the connective tissues between bones and tendons or ligaments. Enthesopathy occurs when these tissues are damaged due to overuse, injury, or arthritis.
Proliferative patellar ligament enthesopathy often occurs with patellar tendinitis – known as jumper’s knee.
Patellar ligament enthesopathy is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
This is an injury to the posterior horn of the medial meniscus associated with anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries. It is a tear in the posterior part of the meniscocapsular junction that can cause knee instability. A ramp lesion often goes unnoticed and requires arthroscopic treatment.
A ramp lesion is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Resection of parapatellar or infrapatellar plica is a surgical procedure that removes synovial structures called plicae located near or below the patella. They can become trapped or irritated due to excessive load on the knee joint.
In arthroscopic resection, the parapatellar plicae, which are located near the lateral edges of the patella, are removed or released, while the infrapatellar plicae lie just below the patella.
Rehabilitation after knee arthroscopy is successfully provided as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is an important band of connective tissue on the lateral side of the knee. LCL tears usually heal after three to 12 weeks, depending on the extent of the injury.
A lateral collateral ligament rupture is a knee injury that causes pain, swelling, and instability of the knee. The ligament connects the shinbone to the thighbone and prevents the knee from bending abnormally outward.
Athletes who participate in sports such as football, American football, and skiing are at higher risk for LCL tears. In most cases, specialised physiotherapy treatment is successful if you decide to seek treatment promptly after the injury.
An LCL rupture is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
Medial collateral ligament (MCL) rupture is a common knee injury. It most often occurs in individuals who play sports such as football, basketball, and skiing.
This is an injury to the medial collateral ligament, which is one of the four main ligaments of the knee, and is located on the medial side of the joint. A tear can be partial (some fibres in the ligament are torn) or complete (the ligament is completely separated).
Most MCL tears heal perfectly without surgery. However, if you have other knee injuries along with an MCL tear, you will likely need surgery, followed by physiotherapy rehabilitation.
An MCL rupture is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
This is similar to Osgood-Schlatter disease, but affects the lower part of the patella where the patellar ligament attaches. The condition occurs primarily in young athletes and causes pain and tenderness in the bottom of the patella.
This disease is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
It is a rare avulsion fracture of the lateral condyle of the tibia, usually associated with anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries. A Segond fracture is an important diagnostic sign for ACL injuries and is often seen on X-rays as a tiny bone fragment on the lateral side of the tibia.
Knee injuries are successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
This is a thickened and inflamed synovial fold that runs from the lower part of the patella towards the intercondylar fossa. It can cause pain and a feeling of tightness in the knee, especially when bending and extending.
This condition is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
A Stieda fracture is an avulsion injury to the medial collateral ligament (MCL) at its attachment to the medial condyle of the femur. This injury is rare and usually results from direct trauma or overextension of the knee.
A Stieda fracture is successfully treated as part of the MEDICOFIT specialist physiotherapy for the knee.
Book a diagnostic therapy appointment for the knee >>
A patella fracture is a fracture of the small bone located at the front of the knee. Because the patella acts as a shield for the knee joint, it is vulnerable to fracture if you fall directly on your knee or, for example, hit the dashboard in a car accident. A patella fracture is a serious injury that can make it difficult or even impossible to straighten the knee and walk.
Some simple patella fractures can be treated with immobilisation and rehabilitation. In most patella fractures, the pieces of bone are displaced from their original position during the injury, and surgery is required to restore and stabilise the knee joint and allow for the return of function.