Foot pain is a common symptom affecting individuals of all ages. The location of foot pain is key to understanding the causes and correctly diagnosing your problems.
Different parts of the foot, such as the heel, toes, instep, ankle, and arch, can become a source of pain for a variety of reasons, including overuse, injury, inflammation, and chronic conditions.
WHEN TO OPT FOR MEDICOFIT DIAGNOSTIC THERAPY?
- When foot pain after an injury or overuse lasts longer than 14 days, it is necessary to undergo diagnostic therapy.
- When you are unable to bear full load on your foot or you have limited mobility because of pain.
- If you have previously had problems with your foot or ankle and the symptoms are recurring, this could mean that the injury was not properly treated or that a new injury has occurred.
At MEDICOFIT clinic, we provide patients with foot pain with scientifically supported specialist physiotherapy, which begins with booking a diagnostic therapy appointment.
Below we present the most common causes of foot pain, depending on where it occurs.
Heel pain
Plantar fasciitis
The plantar fascia is a wide layer of connective tissue that covers the underside of our foot. Its main function is to provide stability to the arch of the foot during movement, such as walking or running, and to absorb the forces generated during activities.
When tension in the fascia and stresses on it increase, small tears can appear in the fascia. Repetitive load on the damaged fascia can cause more of these tears, which irritates the tissue and leads to inflammation called plantar fasciitis.
The risk of developing plantar fasciitis increases in persons with increased body weight, certain abnormal walking patterns, and with age. Persons with high or flat arches and abnormal walking patterns are more prone to developing plantar fasciitis, as this affects the uneven distribution of weight on the foot, which can put additional strain on the plantar fascia.
Symptoms of plantar fasciitis manifest as a sharp or dull pain in the heel area, which may spread further along the entire sole. The worst pain is present in the morning or when the foot is under heavy loads (walking, running, jumping).
Did you know that chronic inflammation of the plantar fascia can also cause a growth called a “heel spur”, which irritates the tendon and causes pain in the sole of the foot?
The key is to successfully treat the problem and reduce the risk factors for recurrence. At MEDICOFIT clinic, treatment includes special stretching techniques, exercises to strengthen the foot, establishing correct walking biomechanics, and instrumental therapy to accelerate tissue regeneration.
Heel spur
A heel spur is the term for a bone spur (osteophyte) that forms due to calcium deposits in the heel area. It can appear in a pointed, hooked, or shelf-like shape. It typically occurs in two places: on the back of the heel or on the bottom of the heel.
A dorsal heel spur occurs where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel bone, while the plantar heel spur occurs at the attachment point of the plantar fascia.
A heel spur is caused by long-term plantar fasciitis (inflammation of the fascia that covers the entire foot) or chronic inflammation of the Achilles tendon.
Symptoms of a heel spur include sharp pain, which is typically worse in the morning when the foot is put under pressure after resting. The pain usually decreases with mild loads (light walking), while increased physical activity significantly increases the pain and worsens the condition.
Did you know that surgical treatment of heel spur is only necessary in approximately 5% of patients? The vast majority of heel spur cases are successfully treated with specialised physiotherapy.
At MEDICOFIT clinic, we recommend at least 16 weeks of physiotherapy treatment before considering surgery. Patients who begin treatment later than the first year after the onset of the problem require longer rehabilitation, even up to 30 weeks.
Achilles tendinitis
Achilles tendinitis is the term used for an inflammation of the Achilles tendon – the strong tendon that connects the calf muscle to the heel bone. The Achilles tendon is essential for foot movement (heel lifting, walking).
Achilles tendinitis occurs due to overuse, repetitive microtrauma, or as a result of tendon degeneration due to ageing processes. Risk factors for its occurrence include excessive exercise (without proper warm-up), inappropriate footwear, flat or high arches, and older age.
The main symptom of Achilles tendinitis is pain and swelling just above the heel, in the area of the Achilles tendon. Heel pain usually worsens during activity – walking up stairs or running.
Treatment for tendinitis usually involves a combination of rest and specialised physiotherapy, with special exercises to strengthen and stretch the tendon. Therapy is also performed with physiotherapy devices that have anti-inflammatory, analgesic and healing effects.
It is important to recognise the signs of Achilles tendinitis in time, as timely physiotherapy treatment can help prevent further complications and speed up your recovery.
Book an appointment for foot pain treatment
Metatarsal pain and foot arch pain
Morton’s neuroma
Morton’s neuroma is a term for a condition where a nerve in the foot becomes thickened (neuroma). Neuroma most often occurs on the foot between the 3rd and 4th toes and causes a sensation that many describe as like standing on a pebble or small ball.
It most often occurs after the age of 40 and is slightly more common in women. The most characteristic symptom of Morton’s neuroma is a sharp pain in the foot, which may be accompanied by tingling and prickling sensations (occurring as a result of compression of the plantar nerve).
The main cause of Morton’s neuroma is pressure or irritation of the nerve because of compression of the toe bones or excessive load on the foot. Some risk factors include:
- Inappropriate footwear: Narrow or high-heeled shoes.
- Overuse: Prolonged standing or walking, especially on hard surfaces.
- Foot deformations: Abnormal walking patterns or deformities (such as flat feet).
- Injuries: Previous foot injuries can increase the risk of Morton’s neuroma.
Morton’s neuroma requires specialised physiotherapy treatment, which at MEDICOFIT clinic includes manual therapy, instrumental therapy, and tailored physiotherapy training.
Metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia is a medical condition that describes pain and discomfort in the area of the metatarsal bones of the foot – the bones in the middle of the foot, between the ankle and the toes.
The pain usually occurs in the area near the base of the toes (ball of the foot) or in the middle of the foot. There is often swelling or tenderness in the toe area, and calluses or hard skin are also often present at pressure points, which can be very painful.
Did you know that pain is usually worst in the summer months? In the summer, we often wear sandals and flip-flops, which do not provide optimal support for the foot.
Metatarsalgia often occurs due to inappropriate footwear (shoes that are too narrow and too stiff), increased load on the feet (sports activity), anatomical deformities of the feet (flat feet), arthritis, or previous injuries to the metatarsal bones.
The diagnosis is made based on a clinical examination of the foot, with diagnostic X-rays recommended in cases of injuries or deformities. Treatment is usually conservative – advice on the use of orthopaedic insoles and using various physiotherapy techniques.
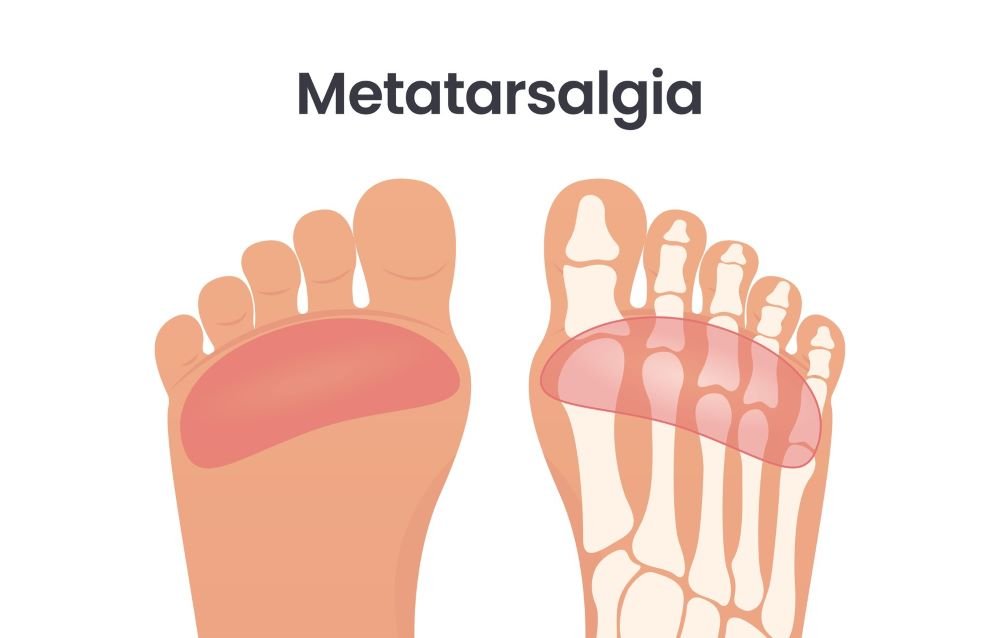
Pain in the bottom of the foot
Flat feet
Flat feet (Latin: pes planus) are an orthopaedic condition where the arch of the foot flattens, causing the entire foot to touch the ground. This can cause a variety of problems and discomfort, including foot pain.
Flat feet can develop due to a variety of causes, including genetic predispositions, foot injuries, age, rheumatoid arthritis, or other diseases that affect the joints and ligaments in the foot.
Pain because of flat feet can occur in several locations. Pain on the inner part of the foot can occur due to pathological load on the foot, where the arch of the foot should be located. Flat feet can also contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis, which causes heel pain.
Individuals with flat feet often experience foot pain during activities (walking and running), as flat feet alter the biomechanics of movement.
Treatment of flat feet at MEDICOFIT clinic begins with advice on suitable footwear – we recommend wearing orthopaedic shoes or insoles that provide support for the arch of the foot. The key part of treatment is physiotherapy, which is aimed at strengthening the muscles of the foot and ankle and establishing correct biomechanics of walking.
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is a medical condition where the structures located in the tarsal canal become compressed. The tarsal canal is a narrow passage located on the inside of the ankle (medial malleolus), through which the veins and nerves that supply the foot pass.
The main structures that pass through the tarsal canal are the tibial nerve (nervus tibialis), the posterior tibial artery (arteria tibialis posterior), numerous veins and the tendon-ligament complexes of the foot.
Due to compression of the structures, typical symptoms occur, which usually include pain on the inside of the ankle (spreading throughout the sole), a feeling of numbness and tingling in the foot (especially the first three toes).
Pain and symptoms depend on the location of the nerve compression. In severe cases of compression, muscle weakness may also be present due to impaired transmission of nerve signals.
The cause of tarsal tunnel syndrome is not always easy to determine. A higher risk of occurrence is seen in flat feet and excessive loads on the ankle and foot (with high activity, local swelling and compression of the tibial nerve may occur).
Did you know that compression in the tarsal canal can also occur due to the formation of nerve cysts or ganglions? Ganglions are often present between the bones of our palms, but they can appear anywhere in the body, including in the tarsal canal.
At MEDICOFIT clinic, the main goal of tarsal tunnel syndrome treatment is to eliminate the cause of the compression and allow the area to heal naturally, thereby reducing pain and inflammation. Before considering invasive procedures such as surgery, it is advisable to first try conservative treatment methods, which include specialised therapeutic exercises, nerve and bone mobilisation, and instrumental therapy, which accelerates healing.
Toe pain
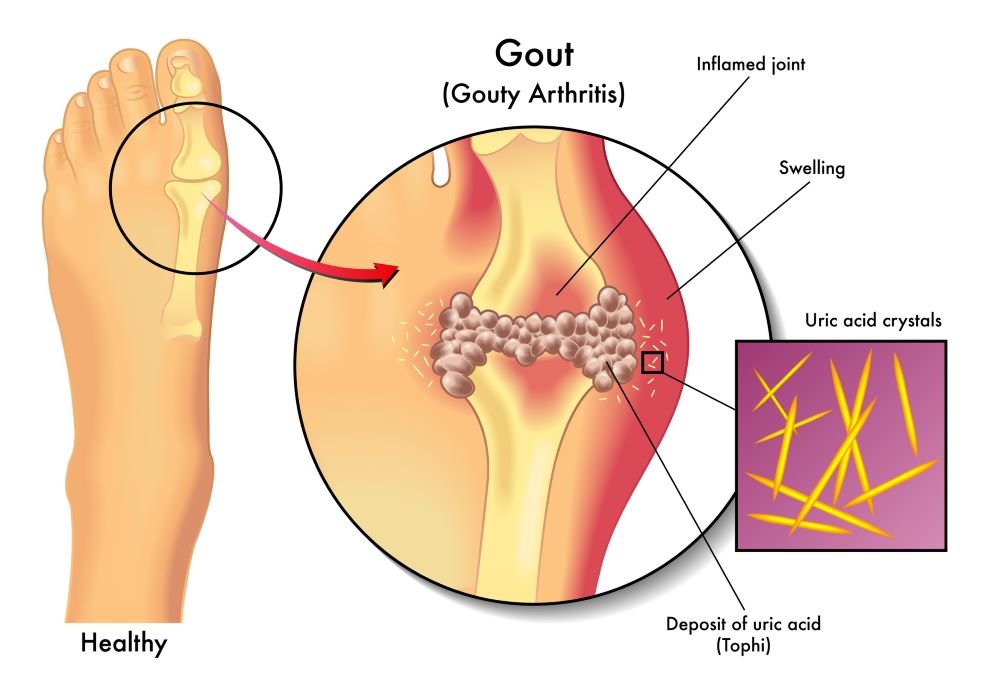
Gout
Gout (also known as uric arthritis) is a medical condition caused by the accumulation of uric acid (in the form of crystals) in the body and can cause severe pain and joint inflammation (arthritis), including in the joints of the toes. Gout occurs when uric acid, which is normally present in the body as a metabolic waste, accumulates in the form of crystals in and around the joints.
Did you know that gout usually affects the big toe first? In medicine, we call this condition “podagra”.
The main symptoms of gout include:
- Severe pain: Acute, sharp pain in joints often occurs, usually starting in one joint, commonly in the big toe, and may spread to other joints. The pain is at its worst a few hours after the attack begins.
- Swelling and limited mobility: The joint is swollen, red, hot to the touch, and very painful.
- Burning sensation and itching: Sometimes you may experience a burning sensation or itching in the affected area.
Gout is usually the result of disorders in the metabolism of uric acid or its increased production in the body. Risk factors for developing gout include excessive consumption of purine foods (red meat, alcohol, legumes, fatty foods), genetic predisposition, being overweight, and high blood pressure.
Treatment for gout usually includes medications to relieve pain and inflammation, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and medications to reduce uric acid levels in the body (allopurinol).
It is also important to change eating habits to reduce the consumption of purine foods and alcohol, and to maintain a healthy lifestyle that includes exercise and a balanced diet.
With proper treatment of the disease, gout attacks rarely occur, which is key to avoiding damage to joints or other tissues. Long-term untreated disease results in permanent joint damage and can cause severe disability.
Book an appointment for foot pain treatment
Arthritis
Arthritis is a general term for a large group of diseases that all involve joint inflammation. Joint inflammation is a process that can affect any joint in the body, including the joints in the toes.
The main symptoms of arthritis are pain, swelling, limited mobility, and stiffness in the toes. As the disease progresses, arthritis can cause permanent deformities of the toes (curled toes). This can significantly affect the ability to walk and perform many activities.
Arthritis in the toes can be caused by many forms of arthritis, the most common of which are rheumatoid arthritis, arthrosis (osteoarthritis), and psoriatic arthritis.
Did you know that dactylitis occurs in psoriatic arthritis (present in psoriasis)? Dactylitis is a term that describes diffuse swelling of the entire toe. The toe is thickened and swollen due to inflammation of the small joints and tendon sheaths.
Arthritis is usually diagnosed based on a clinical examination, imaging studies (X-rays), and laboratory tests to determine inflammatory markers.
Treatment for arthritis includes anti-inflammatory medications combined with physiotherapy to improve toe mobility and strength, and lifestyle adjustments, which may include dietary changes.
At MEDICOFIT clinic, we are well aware that physiotherapy is a key part of a comprehensive arthritis treatment plan, as it can significantly improve patients’ quality of life, reduce pain, and increase joint function. An individual approach and tailoring therapy to the specific needs of each patient are crucial to the success of physiotherapy treatment.
Toe injury
Toe injuries, such as sprains and fractures, are relatively common injuries that can occur while doing everyday tasks or during sports activities.
A toe sprain occurs when the ligaments that connect the bones are stretched or damaged. This usually occurs as a result of sudden movements, a blow to the toe, or in sports that require quick stops or changes of direction (football, basketball).
Symptoms of a sprained toe include pain at the site of the injury, swelling and bruising, and limited mobility of the toe. Sprains are usually treated with rest and ice, but for more severe sprains, physiotherapy is recommended to restore optimal toe function.
A toe fracture usually occurs due to a strong blow or fall, where a lot of pressure is applied to the toe. A toe fracture is confirmed with an X-ray, which is followed by immobilisation of the toe – this allows for proper healing and fusion of the bone fragments.
Physiotherapy treatment is crucial for a quick and safe recovery from a sprained or broken toe. Physiotherapy helps manage pain, improve mobility, strengthen muscles, and prevent potential complications after an injury.
Pain throughout the entire foot
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various joints in the body, including the joints in the feet. Pain throughout the foot is one of the possible symptoms of this disease.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, where the immune system attacks the joints of one’s own body, causing inflammation of the joint lining (synovium), pain, swelling, and joint damage.
In addition to pain, symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include morning stiffness, limited joint mobility, and swelling in the joints. Our patients also often complain of general fatigue and malaise.
Did you know that rheumatoid arthritis often presents symmetrically? This means that both feet can be affected at the same time.
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect any joint in the foot, including the joints of the ankle, midfoot, and toes. Untreated rheumatoid arthritis in the foot can cause permanent joint deformities and changes in gait.
Physiotherapy, along with anti-inflammatory medications, is a key part of the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in the foot. Working together with a physiotherapist, you will perform special exercises to maintain foot mobility and strength, as well as correct walking techniques.
Osteoarthrosis
Osteoarthrosis (also called osteoarthritis) is the most common degenerative disease affecting articular cartilage. Cartilage wears down and changes its structure over the years, which can lead to severe joint pain and difficulty walking.
Osteoarthrosis mainly affects joints that are under heavy load, among them the joints of the feet. Symptoms of foot arthrosis include foot pain (worst in the morning and after prolonged rest), limited mobility in the foot, with possible swelling or visible deformation of the foot bones.
There are many known risk factors for the development of arthrosis in the foot, the most important being age (cartilage changes with age), genetic (familial) predisposition and previous injuries to the foot (sprains or fractures in the foot area significantly increase the risk of developing arthrosis).
Did you know that osteoarthrosis in the foot can also occur as a result of obesity? Excessive weight causes additional pressure and load on the joints of the feet.
Unfortunately, osteoarthrosis cannot be cured, but we can slow its progression. Physiotherapy treatment is indispensable for all types of joint wear, as it improves mobility, stability and muscle strength, and successfully reduces foot pain. Timely diagnosis and active physiotherapy treatment can help slow the progression of the disease and improve your quality of life.

Tendinitis
Foot tendinitis is a medical condition where one or more tendons in the foot become inflamed. Tendons are strong connective bands of tissue that connect muscles to bones. Foot tendinitis is usually caused by overuse, but it can also be the result of an injury.
Are there different types of foot tendinitis? The human foot contains many tendons, and tendinitis can affect any of them, but the most common are:
- Achilles tendinitis: It affects the tendon that connects the calf muscle to the heel bone. This tendon is the strongest tendon in the body and allows us to run, jump, walk, and do other activities that require us to stand on our toes.
- Extensor tendinitis: Irritation of a group of tendons that run along the top of the foot. These tendons connect the bones of the front of the leg to the toes.
- Peroneal tendinitis: Inflammation of one or both tendons that run along the outside of the ankle. They connect to the arch of the foot and help maintain stability when walking.
- Posterior tibial tendinitis: It affects the tendon that connects the calf muscle to the bones on the inside of the foot. These tendons help maintain the arch of the foot and provide stability when walking.
Treatment for tendinitis depends on the location and severity of symptoms. The first step is usually rest – limiting activity and avoiding activities that cause pain.
Physiotherapy treatment is key to faster recovery, improving foot mobility, strengthening muscles and tendons, improving foot stability, and using anti-inflammatory treatment to reduce inflammation and accelerate tendon healing
Book an appointment for foot pain treatment
At MEDICOFIT clinic, we are specialised for treating all musculoskeletal conditions that cause foot pain. Our comprehensive treatment plan is tailored to each individual and consists of four phases: diagnostic examination, acute physiotherapy, post-acute kinesiology, and preventive kinesiotherapy.
Diagnostic therapy
The basis of any treatment is a good diagnostic examination to assess the patient’s condition. The physiotherapist will have an in-depth discussion with you about the nature of your problems and will perform a clinical examination.
The examination involves inspection and palpation of the entire foot and ankle – we look for skin changes, foot deformities, and the presence of swelling and inflammation.
We perform active and passive mobility tests to distinguish between muscular and mechanical causes of limited mobility.
We asses muscle strength and performance, looking for any muscle imbalances or muscle weakness.
Because the feet bear the entire load of our body, pathologies in this area can significantly affect biomechanics and walking pattern, as well as posture.
In the event of a suspected nerve compression, we perform special neurological tests that help us assess nerve function in the foot.
We also conduct specific tests that are known for certain diagnoses (Mulder’s test, Tinel’s test, and others).
If necessary, the diagnostician may suggest additional diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging.
Based on the findings of the diagnostic examination, we will prepare an individualised treatment plan for you.
Acute physiotherapy
In the acute phase of treatment, physiotherapists will focus on controlling your symptoms – reducing foot pain, any swelling and tissue inflammation, and improving mobility.
In the acute phase, we perform manual therapy, joint mobilisation, soft tissue mobilisation, nerve mobilisation, and trigger point therapy.
We combine physiotherapy techniques with instrumental therapy, which is performed at MEDICOFIT clinic using state-of-the-art physiotherapy devices. The devices we use are:
- Wintecare TECAR therapy,
- Summus high-energy laser therapy,
- Ultrasound therapy,
- 6D action, and
- HiTop high-tone electrostimulation.
Instrumental therapy has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, increases blood circulation in tissues and accelerates natural healing processes, even deep within the body. Which therapies are right for you will depend on your diagnosis.
Once the pain has sufficiently decreased, we focus on performing special physiotherapy exercises aimed at strengthening the foot muscles and performing movements correctly.
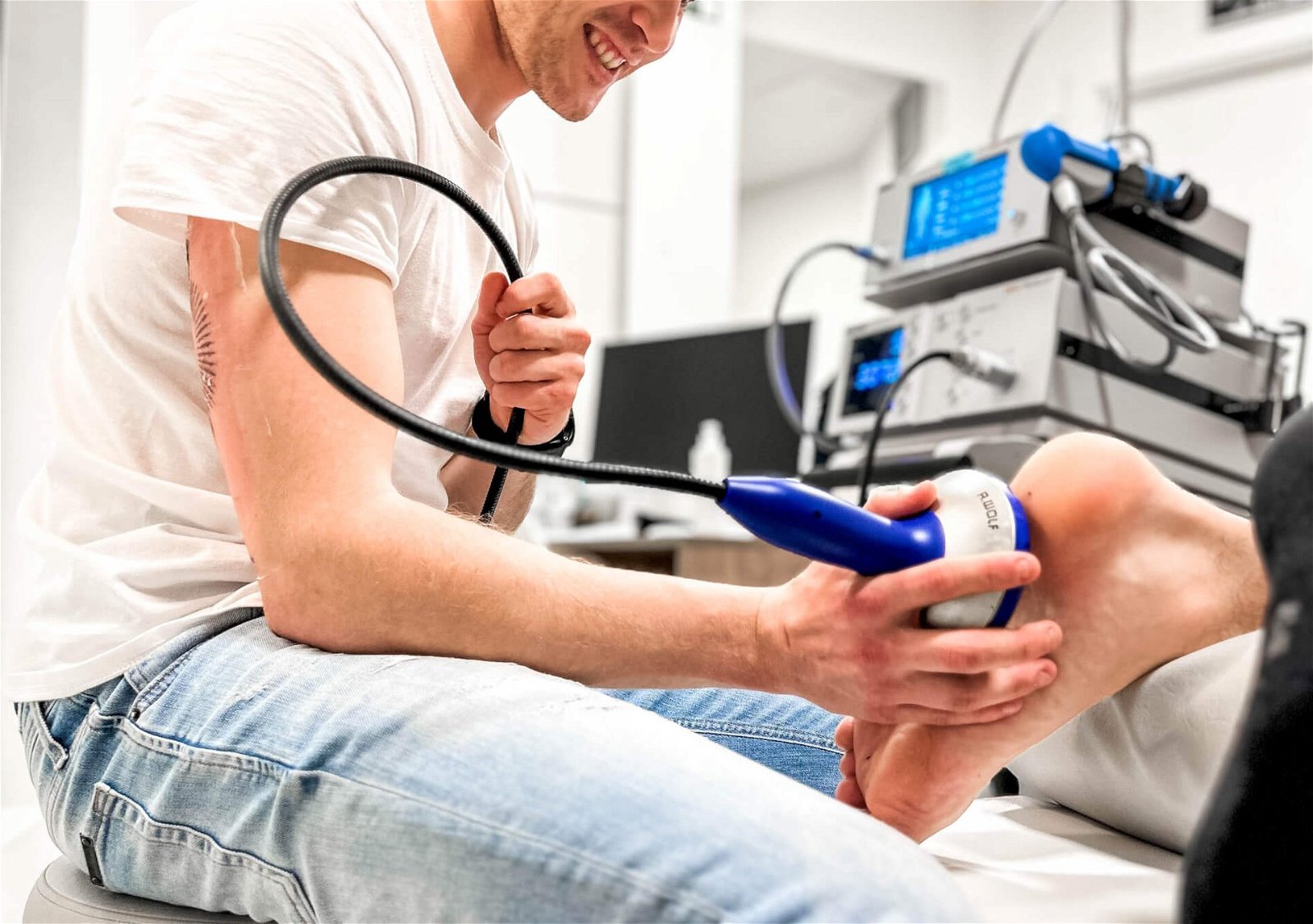

Post-acute kinesiology
After the physiotherapy phase, you will be guided through the next part of the treatment by kinesiology experts.
We will prepare a kinesiology programme of special training tailored specifically for you, where we will achieve perfect symmetry and optimal muscle strength of the flexors and extensors of the foot.
With expert training, we will achieve optimal foot mobility, and also establish better balance and improve proprioception.
Once full range of motion is achieved, the training will be focus on strengthening the entire lower extremity and core stabilisers.
The training will be tailored to your abilities and will progressively increase over time. Once the goals are achieved, we will include more complex motor exercises and special plyometric training in the training.
Before completing the treatment, kinesiologists will also conduct a test battery for your foot, where we objectively check the effectiveness of the treatment and further increase your confidence when applying load to your foot.

Preventive kinesiotherapy
After successfully completing the treatment of foot pain, our patients participate in a post-rehabilitation programme, aimed at maintaining optimal foot function and preventing recurrence of the disease.
The preventive programme focuses on maintaining muscle strength and strengthening the entire body, not just your feet, which has a positive effect on all joints.
With our preventive programme, we also effectively prevent the occurrence of new injuries or the progression of wear and tear on the joints in your feet.
At MEDICOFIT clinic, we follow the latest guidelines for treating the causes of foot pain while focusing on comprehensively improving your health and well-being.
Because we believe in a comprehensive treatment, we restore full strength and movement function to your feet and guide you to free movement without pain.
DANGERS AND PITFALLS OF DELAYED REHABILITATION

MEDICOFIT specialists
- Untreated joint injuries can cause degenerative changes and the development of arthrosis, leading to permanent disability.
- Without proper treatment, deformities such as hallux valgus, hammer toes, and flat feet lead to more severe movement limitations.
- Prolonged pressure on nerves, as in Morton’s neuroma or neuropathy, can cause permanent neurological damage, leading to motor dysfunction.
Inadequate or delayed rehabilitation seriously jeopardises an individual’s long-term physical health and is the main culprit for unsuccessful results and permanent movement limitations.